What is radon and how can I be exposed?
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that occurs when uranium, thorium and radium break down in soil, rock and water….. that is the boring and scientific section of this article! What home owners and buyers need to know is that radon is odorless, tasteless and invisible; it accumulates in places with inadequate ventilation and long-term exposure to high levels of radon can be dangerous to your health.
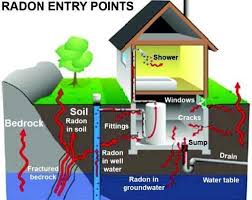
You are exposed to radon through the air you breath. Radon enters the home through cracks in the foundation or through the exposed earth of the crawl space floor. It is estimated that one in 15 homes have high radon levels because once it’s in the home it can be trapped where it builds up. It doesn’t matter if the home is on a slab, has a basement or a crawl space.
Higher levels of radon are more likely to occur in homes that are tightly sealed, heavily insulated and / or located where high levels of uranium, thorium and radium are found in the soil. The highest levels of radon concentration are usually found in the lower levels of the home.
What are the effects of radon exposure?
According to EPA estimates, radon exposure is a leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers. They estimate that radon is responsible for approximately 21,000 lung cancer deaths every year with about 2,900 of these among people who have never smoked.
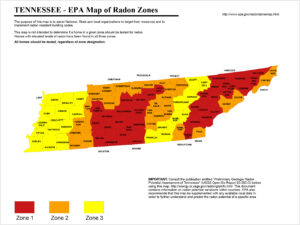
According to the EPA East Tennessee averages in most counties are over the mandated mitigation level of 4.0 pCi/L which means approximately 62 out of 1000 smokers could get lung cancer – 5 times the risk of dying in a car crash (from A Citizen’s Guide to Radon)
WHAT SHOULD YOU DO?
First and foremost, you should get your home (or the home you are considering buying) tested. This is a simple test that most home inspectors can perform as an additional service during the inspection process or as a stand alone test. The house should be kept in closed conditions (which the inspector will detail) before the test which then takes 48 hours to complete. The most popular testing devices are continual monitoring which will provide an hourly reading of radon levels and an average for the 48 hour test period; and charcoal cannisters, which are placed in the home for 48 hours and sent to a lab to obtain an aggregate average but no hourly readings. Most consider the continuous monitor to be the better of the two test methods because of accuracy, difficulty in tampering with the device and timeliness of the report.
Depending on the level of radon found the solution may be as simple as sealing and caulking foundation cracks/openings that can allow radon to enter; installing heavy plastic sheeting over the crawl space floor or enlisting the help of a radon mitigation contractor to install a more sophisticated radon mitigation system. Regardless of the method of mitigation, ALWAYS get a verification test after the modifications are made and continue to do periodic tests to insure radon levels stay within acceptable limits.
Feel free to contact us if you would like to know more about radon testing or to schedule your radon test.